How to Check if a Link Is Safe: 6 Effective Methods to Check URL + Secure Browsing Tips

Cyber criminals often use malicious links for phishing attacks or malware infections. Clicking such links can expose you to various security threats, from identity theft to stolen sensitive information. This is especially important for online shop website owners.
Attackers may use different mediums to send the links, including emails, social media posts, and personal messages. They also make the links look legitimate and believable to allure users to click them.
Thankfully, you can distinguish malicious links using various methods. In this article, we will explain how to check if a link is safe to help you browse more safely.

How to Check if the Link Is Safe in 6 Ways
In this section, we will go over six ways to detect potentially malicious websites. For a more accurate analysis, we recommend combining all methods.
1. Use a Link Checker Tool
Use link checkers to check whether the website is safe. These web-based tools are completely free, easily accessible, and simple to use.
URLVoid is a popular link checker tool. It uses blocklist databases and online website reputation services to check unsafe links. Other notable URL checker tools include:
To see if a link is safe, access the tool on your browser and copy-paste the URL into the designated field. You may use a shortened or permanent URL.
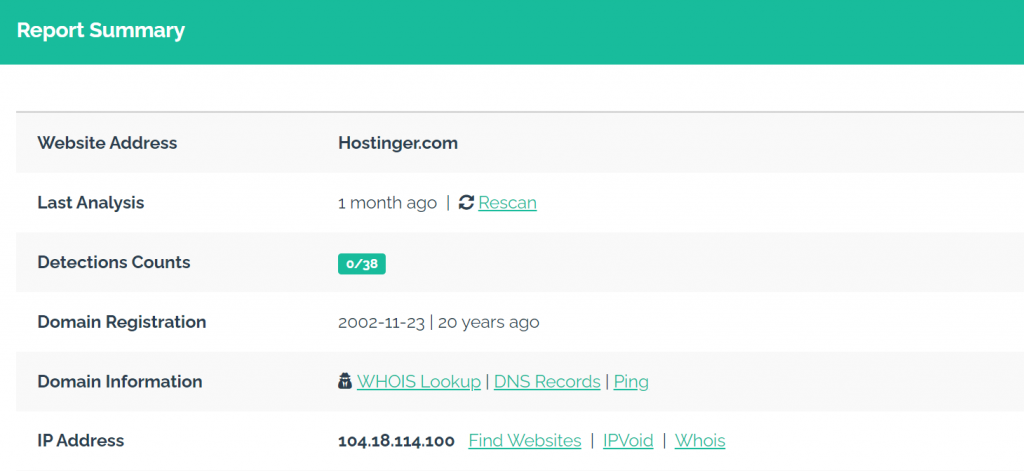
The tool will provide a safety report and warn you if the link contains malicious content.
2. Make Sure the Site Uses HTTPS
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is a method that enables data transmission between a website and its visitors’ browsers. Meanwhile, Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is its safer version.
Unlike HTTP, HTTPS uses a secure socket layer (SSL) or transport layer security (TLS) to secure data transmission. These certificates verify the website’s server authority and encrypt the transferred data.
Data transferred through the secure protocol is obscured until an SSL/TLS certificate decrypts it. Even if hackers gain access to the transmission, they can’t retrieve the actual data.

Look for HTTPS at the beginning of a site’s URL to check if it uses the most secure protocol. Avoid opening HTTP links since they are more likely to lead to unsafe sites.
3. Look for Legit Contact Information
If you receive a suspicious link from emails or private messages, always check the sender’s contact information. It is because cyber criminals may impersonate your colleague’s or a company’s contact details.
This strategy makes the phishing link more convincing to entice unwary users to enter their personal data. Furthermore, they also design the phishing website to resemble the original one.
Look for legitimate contact information to verify if the visited website is safe. Check if the website provides an email, phone number, and real address.
Websites without this important information are more likely to be fraudulent. Also, a fictional or vague address may signify a phishing site.
4. Examine Google Reviews
Look up Google reviews of a suspicious website to help verify its safety. In addition to Google, examine testimonials in blogs, social media, or review websites such as Trustpilot.
However, note that sometimes user reviews are not an accurate indicator of a website’s safety. Since users may fabricate their reviews, be more careful when examining them.
Some reviews may be dishonest and aim to deceive visitors or ruin competitors’ reputations. Also, several legit websites may lack positive reviews because they are still new.
Check the reviewers’ profile page to verify their testimonials’ legitimacy. In addition, reviews that sound unnatural and follow a certain template are most likely not accurate.
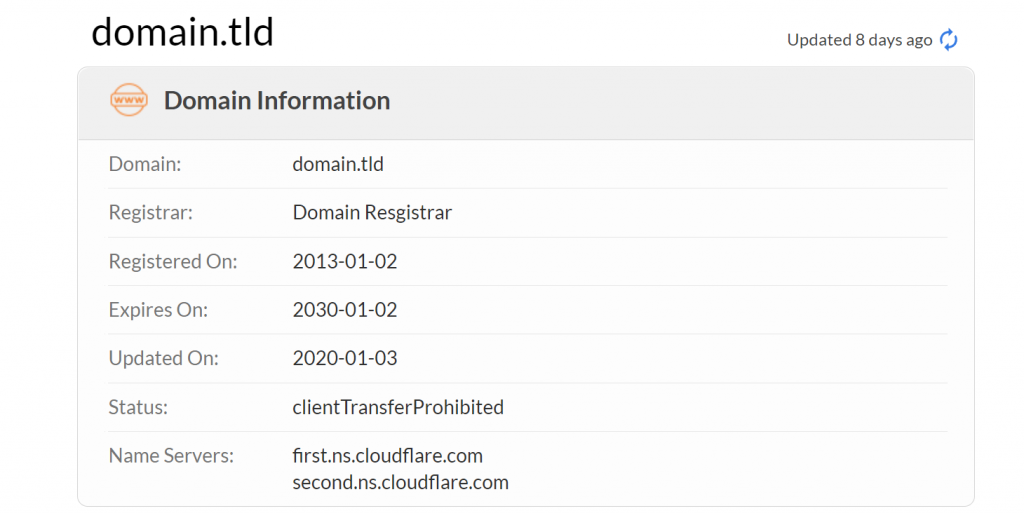
5. Check the Domain Age and Ownership
To verify a website’s safety, check its background using WHOIS search. This tool allows you to find the website owner, registration date, and the registrant’s contact information.
If the domain hides those details, it may be unsafe. However, some websites may hide their information to comply with laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
6. Utilize a Backlink Analysis Tool
A backlink is a URL that leads from one website to another. A website with many backlinks is featured on many other pages, proving its trustworthiness.
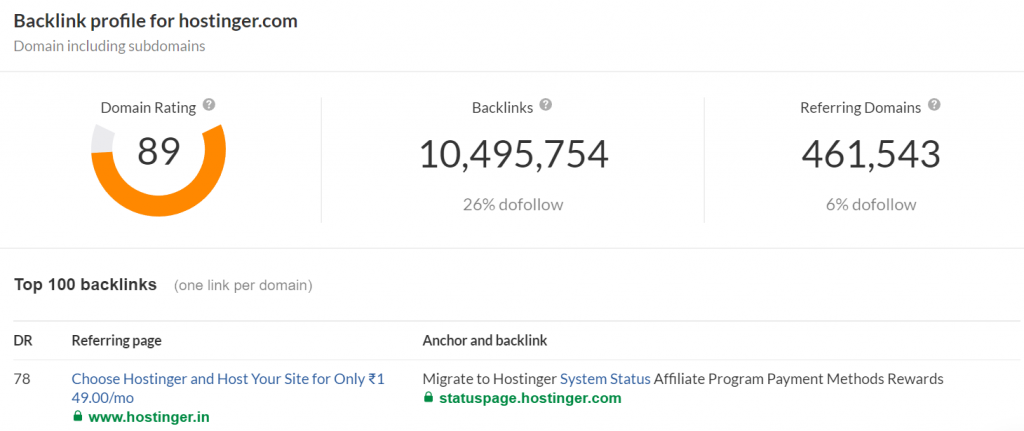
The easiest way to check a website’s backlink profile is to use the Ahrefs site checker tool. Simply enter the website’s URL, and the tool will provide its backlink analysis report.
Tips for Accessing New Links
In addition to performing a thorough check, apply the following tips to help you avoid accessing a compromised website.
Use a VPN
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a service that bridges communication between your browser and a website’s host. It encrypts important data such as your passwords, location, browser history, and IP address.
VPN encryption helps prevent cybercriminals from using your data for unauthorized access and data breach. Visiting unsafe websites with VPN enabled minimizes security risks.
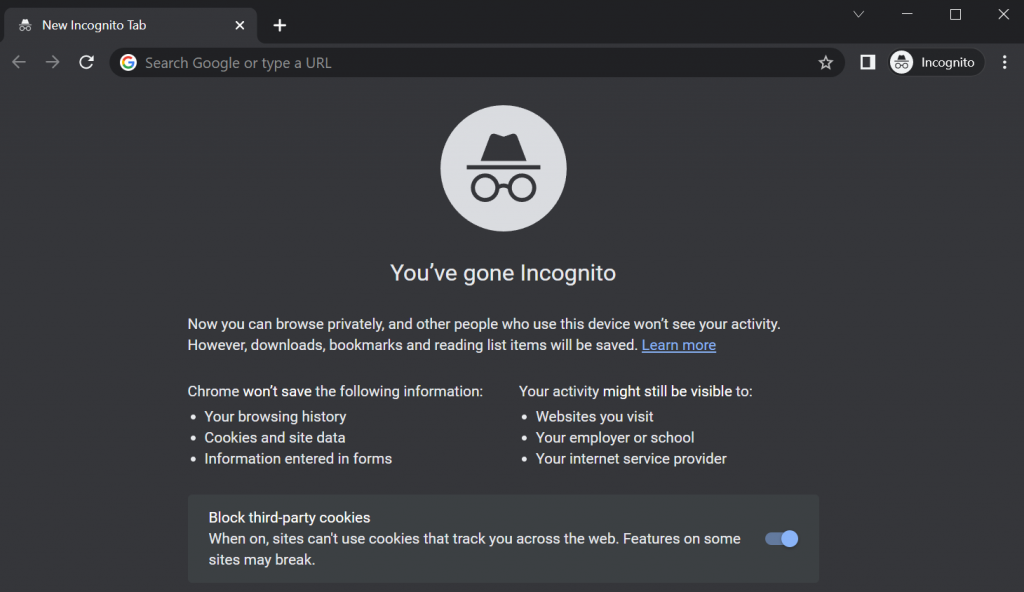
Use Incognito Mode on the Browser
The incognito mode allows you to browse the internet without affecting your user data. It keeps important information isolated in the main browsing session, minimizing data theft risk when visiting a malicious link.
To access the private mode, go to your browser settings or use the shortcut. Since incognito mode doesn’t encrypt or hide important data, we recommend using it with VPN enabled.
Copy and Paste the Link to a Text Editor for Inspection
Cyber criminals often disguise suspicious links using deceiving anchor texts. To check the actual link, copy it by left-clicking the anchor text and pasting it onto a text editor.
They may also shorten an unsafe link to hide the actual URL. In this case, use link checkers or preview the shortened URLs.
Enable the Antivirus’s Active Scanning Options
Your system’s antivirus’s active scanning feature constantly checks for malware and malicious software. It quickly removes threats that infect your system through an unsafe site.
Some antiviruses also warn and prevent you from entering potentially dangerous sites.
Conclusion
Many cyber criminals use unsafe links to infect users’ devices with malware or lure them into phishing sites. These links usually look legitimate, enticing unwary users to click.
Clicking these links exposes you to data safety risks and other security threats. Fortunately, there are various methods to check if a link is safe:
- Analyze the URL using a link checker tool.
- Check for HTTPS in the website’s URL.
- Look for contact information and address on the website or message.
- Examine community reviews of the website.
- Use WHOIS to check the domain creation date and owner.
- Make sure the website is credible by checking the number of its backlinks.
To safely access a suspicious link, enable VPN and antivirus real-time protection. Also, check the actual URL in a text editor and access it using incognito mode.



Comments
January 07 2024
How about, if the site seems suspicious, and it's hosted by Hostinger, then it's likely a phishing site.
January 08 2024
Hi there! Thank you for raising this concern. If you come across a site hosted by Hostinger that seems suspicious or potentially involved in phishing activities, please report it to us at Report Abuse Form. We take such matters seriously and will promptly investigate and take appropriate action. Your vigilance helps maintain a safe online environment ?